Growth of city trees can cut air pollution, says report
A study by US-based The Nature Conservancy (TNC) reported than the average reduction of particulate matter near a tree was between 7% and 24%.
Particulate matter (PM) is microscopic particles that become trapped in the lungs of people breathing polluted air.
PM pollution could claim an estimated 6.2 million lives each year by 2050, the study suggests.
Lead author Rob McDonald said that city trees were already providing a lot of benefits to people living in urban areas.
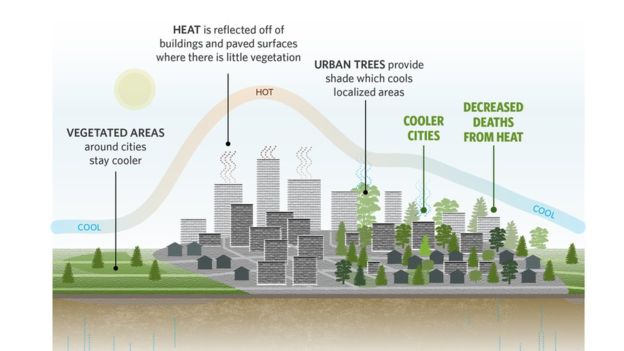
"The average reduction of particulate matter near a tree is between 7-24%, while the cooling effect is up to 2C (3.6F). There are already tens of millions of people getting those kinds of benefits," he said.
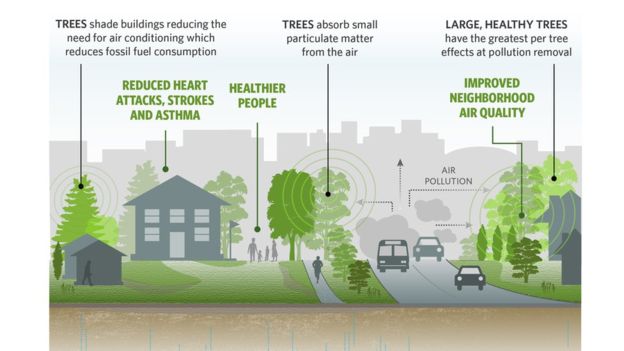 |
Dr McDonald said the study of the use of trees in 245 cities around the world compared the cost-effectiveness of trees with other methods of cooling and cleaning air.
"On that front, trees are cost competitive with other options," he told BBC News.
"When you change a bus from diesel to gasoline, for example, you reduce particulate matter pollution, and trees are certainly in the same ball park."
However, the TNC report highlighted that most of the cities featured in the study were losing more trees than they were gaining.
According to the UN World Health Organization (WHO), about 90% of the global population living in cities in 2014 was exposed to particulate matter that exceeded the WHO air quality guidelines.
The UN agency estimates that outdoor air pollution caused three million premature deaths in 2012, with the vast majority occurring in low- to middle-income nations.
The WHO Health Statistics 2016 says air pollution is "caused by inefficient energy production, distribution and use, especially in the industrial, transportation and building sectors, and by poor waste management".
It adds that transport systems based primarily on individual motorised transport can lead to further deterioration in air quality.
 |
As everyone within an urban area breathes the same air, the pollution does not discriminate - both rich and poor are exposed to the dangers. But, it adds, people living near the source or busy roads are more exposed and more affected.
The WHO says that the air quality in many cities is not monitored, making it difficult to get an accurate understanding of the global impact of air pollution.
Dr McDonald observed: "Trees are by no means a replacement for all the other things cities need to do in order to clean their air but they are part of the suite of tools that cities can draw on.
"We also looked at how much more trees could help if we planted more trees. We found that there was a lot more scope there. All of the cities we looked at, if all the people in them spent an extra US $4 a year on planting trees, you could save between 11,000 and 36,000 lives each year. This is mostly as a result of having cleaner air''.

